Document Workflow Automation for Business Analysts: Learn how to become a business process analyst

Career prospects are one of the most influential factors to consider when deciding on a profession. By 2029, the employment of business process analysts is projected to increase by over 11% (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics). And with good reason – it opens up a range of industries to work in, has lower entry barriers, and offers steady year-over-year career growth.
The digital transformation trend has introduced a shift in terms of future-oriented professions, and business analysts have managed to ride the wave.
As businesses seek innovative solutions to stay competitive, the demand for skilled business analysts, business process analysts, and professionals in adjacent fields is on the rise. If you are already an analyst or aspiring to become one, enrolling in the airSlate Academy certification program on Document Workflow Automation for Business Analysts can significantly boost your career prospects and provide you with a competitive edge in the job market.
In this blog, you’ll get questions like: “what does an analyst do?” or “is business analyst a good career?” answered. Also, learn about business process analyst salary range and responsibilities, and finally – how to become a business process analyst.
How much does a business process analyst earn?
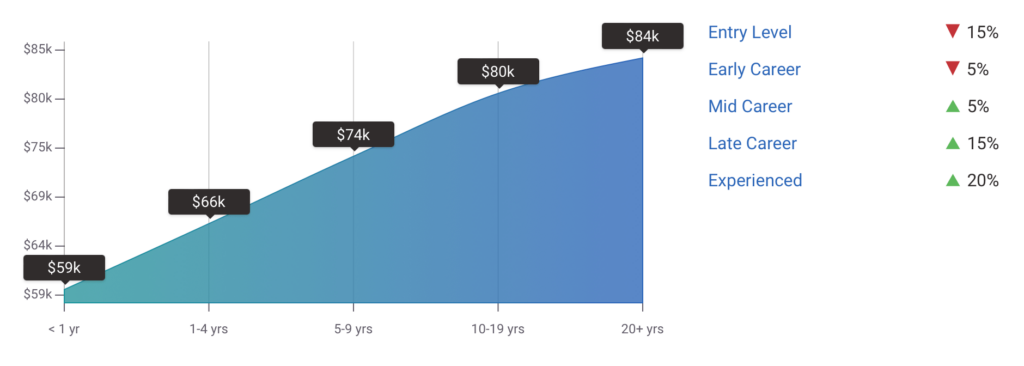
When considering one’s career, the salary range remains one of the most defining factors. As of June 2023, ZipRecruiter reports that the national average salary for a business analyst is $95,472. Glassdoor cites a slightly lower average annual salary of $90,695, while top-level business analysts can expect to earn as much as $135,000 per year.
On the other hand, Zippia presents a more modest median salary of $78,215, which serves as the base pay and can be increased with additional income such as bonuses. The business process analyst salary range is influenced by various factors, including the industry, years of experience in the field of business analysis, and whether the position is full-time or part-time.
Watch the video below to learn more about the position of a business process analyst:
Which factors influence business analyst salary?
Industry
Like in any profession, salary range differs from industry to industry. A business analyst is an in-demand job in finance, IT, retail, manufacturing, healthcare, education, legal, and many other fields. The top 5 most popular industries for business process analysts in the US are Finance, IT, Healthcare, Education, and Legal.
Experience
Clearly, the more years of experience you have, the higher salary you can expect from a potential employer. In the US, the difference between an entry-level business analyst and an experienced one can increase by double or even more.
Types of business analyst jobs
Another important point is that business analysis has a wide range of specializations. Depending on the job responsibilities, these types of analyst jobs include (but are not limited to):
- Business analyst gathers requirements, identifies problems, and proposes solutions to help improve business operations, enhance efficiency, and achieve business objectives. BAs work closely with stakeholders, such as clients, end-users, and project managers, to understand their needs and translate them into functional specifications for IT teams or other departments.
- Business process analyst specializes in analyzing business processes. This includes business process modelling, creating and implementing business analysis into these processes to effect change, especially when new procedures and policies are introduced. The process analyst job implies assessing business requirements and making recommendations to support process improvements. Finally, a BA is also responsible for the overall process performance.
- Process improvement analyst specializes in optimizing business processes within an organization. Their primary focus is to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement in existing processes and workflows. By utilizing various methodologies and data analysis techniques, Process Improvement Analysts aim to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and increase overall productivity. Their role is critical in driving continuous improvement initiatives and achieving operational excellence.
- Data analyst (or data process analyst) primarily gathers and interprets data to solve a specific business problem. This job implies spending a number of hours on data analysis as well as communicating the findings.
- Business intelligence analysts review data that becomes the basis for creating finance and market intelligence reports. Such reports highlight trends and patterns in a selected market which eventually influence a company’s operations and goals.
- Business systems analyst helps organizations operate in a more effective and efficient way by designing and implementing IT systems. These professionals use both business and IT tools to assess an organization’s operating systems and develop improvements.
- Operations analyst reviews and checks policies and procedures, and creates reports with guidelines on how to enhance a company’s operations. Other than gathering information, the responsibilities include identifying operational requirements, the appropriate methods of operations analysis, and more.
The average salary for the above variations of a business process analyst role is as follows:
| Job title | Salary |
| Business system analyst | $99,256 |
| Business analyst | $95,472 |
| Business intelligence analyst | $94,924 |
| Process improvement analyst | $83,557 |
| Data analyst | $80,429 |
| Business process analyst | $74,569 |
| Operations analyst | $66,225 |
In 2023, many professionals began mastering new business process analyst skills in the field of business analysis, like those of the related jobs listed above. This move will allow them to acquire useful knowledge, expertise and soft skills that will eventually turn into a financial benefit.
What does a process analyst do?
So, what is a business process analyst? Evolution is integral to the survival of any organization. As new business objectives are set, new products and services need to be launched and new business processes must be put in place alongside to support them.
With competition becoming more intense, companies are striving to achieve business automation success to thrive in the post-COVID world. Technologies like robotic process automation are becoming more commonplace. Moreover, when a business reaches a certain size, comes the time for process improvement.
A business analyst is typically the engine for that change. Business analysts process high volumes of data to build reports, create new processes to replace existing ones, and consult on how to build a process from the ground up for maximum efficiency.
Business process analyst job description requirements
Here’s an approximate range of responsibilities commonly listed in a business process analyst job description:
- Create reports and presentations that utilize qualitative analyses regarding companies, markets, and industry trends.
- Conduct site observations to identify which methods, equipment, and personnel are necessary for effective processes.
- Prepare financial reports in support of monthly/quarterly business review meetings with senior management and stakeholders.
- Analyze emerging business best practices and technological developments aimed at automating and streamlining processes to increase performance efficiency.
- Collect information and data (for developing better process engineering) through flow-charting, process mapping, and workshops.
- Conduct meetings with clients (to determine their business goals) as well as different stakeholders and participants in various parts of operational processes; conduct business process analysis flows using the revealed information.
- Maintain regular interactions with project controllers, project managers, cost center owners, and accounting personnel to ensure that business operations are closely monitored and potential risks are mitigated.
- Analyze the actual results against budgets and/or forecasts and communicate variances to senior management.
- Gather data, analyze, and make recommendations to meet project objectives, prepare client presentations, and assist in pre-call planning.
- Analyze and review monthly financial results and ensure any identified errors are corrected in a timely fashion.
- Assess business requirements and provide recommendations for process improvement.
Business process analysts are often confused with business analysts. To help you avoid this mix-up, we’ve created a short Business analyst vs. Business process analyst comparison table:
| Business performance enhancement | Process modeling | Analysis tools | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business analyst | Focused on business needs and solution improvement | Requirement analysis | airSlate, ClickUp, Bizagi, Jira, NS Visio, Teamwork, Trello, Zoho |
| Business process analyst | Focused on business processes and their improvement | Process analysis | airSlate, Bizagi, Kissflow, Minitab, MS Visio, ProcessMaker |
Who is a good fit for business process analyst jobs?
Typically, a business analyst’s skills are a mix of technical knowledge and soft skills. Some job listings include a higher education requirement, however, most entry-level jobs in this field, and especially business analyst internships, do not. It’s not a rare case when business intelligence analysts are entirely self-taught, getting all of their education for free on the internet.
Here are just some of the skills and knowledge required to do the job well:
- Research – skilled researchers will be valuable in pretty much any role, but business analysts can especially benefit from understanding how other organizations work. This skill will also come into play when conducting internal research on how any given part of a company functions from day to day.
- Analysis – once the research is out of the way, it’s time to analyze. BPAs are well aware of what the business analysis process is and what it consists of. To that end, process analysts will benefit from understanding process mapping as a method of visualizing an ongoing process. It’s an extremely helpful tool that shines light on inefficiencies and other problem areas within the scope of what is called a business workflow.
- Communication – not only will this help conduct the interviews mentioned above but many problems can be solved by communicating. Often enough, different parts of a company will speak different languages, acting as if they’re pursuing different goals. Helping facilitate that communication can deliver value and stand out in the overall results.
- Education – most positions in this field will require a certain range of skills rather than a specific degree, with automation being the newest and most valuable. In fact, it is more likely that an employer will not look for a specific degree, but rather a Business Process Analyst Certification.
- Document Workflow Automation for Business Analysis – automation in the workplace is no longer something we talk about as a feature of the future, but more as a necessity of the now. More on this below.
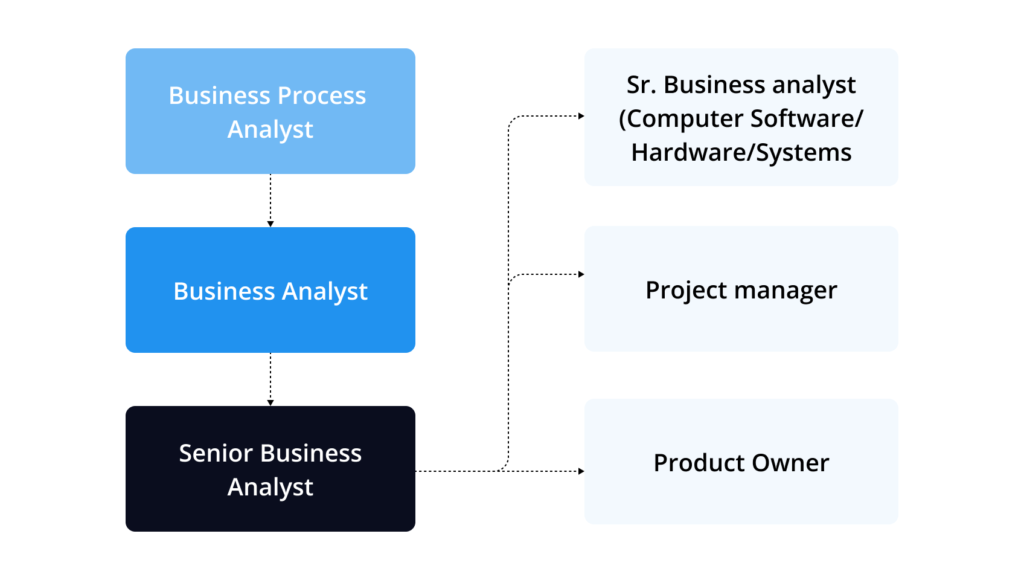
These competencies will not only make you a perfect fit for a process analyst job description but also move up the career ladder. For example, in the IT industry, a career path for business analyst may look like this:
What does the Document Workflow Automation for Business Analysts certification cover?
This certification program is the perfect option for those looking to obtain business process analyst qualifications. Students will learn how to get the most out of a business by reducing the amount of time and money spent on routine processes.
The Document Workflow Automation for Business Analysts certification program at the airSlate Academy will teach you valuable insights on identifying and tackling complex workflows by leveraging the power of automation.
Upon successful completion of this certification program, you’ll unlock the potential to enhance both efficiency and accuracy in your daily tasks. As a testament to your newfound expertise, you’ll also be awarded a prestigious digital certificate.
The certification program explores:
- The significance of document workflow automation and its role in transforming business operations.
- How document workflow automation streamlines intricate business processes, resulting in increased productivity.
- Step-by-step guidance on constructing fully automated workflows without the need for coding expertise.
By the end of the certification program, you’ll have acquired skills in data collection, workflow optimization, and overall business process efficiency, empowering you to excel in your professional endeavors.
Other free online courses at the airSlate Academy that might be helpful to business analysts:
- airSlate Workflow Analytics reveals how to ensure internal business processes are functioning effectively, which analytics tools and metrics can be adopted, and ways to determine areas of improvement. Students will learn more about the methods, mechanisms of data collection, analysis, exporting, and what makes analytics part of a business process.
- Introduction to Document Process Automation helps students stay in the know on Document Process Automation (DPA), Business Process Automation (BPA), and the correlation between the two. Students will learn how to distinguish between different solutions designed for automating business processes and observe multiple options for task optimization so that they can help a business rededicate time and money towards other vital goals.
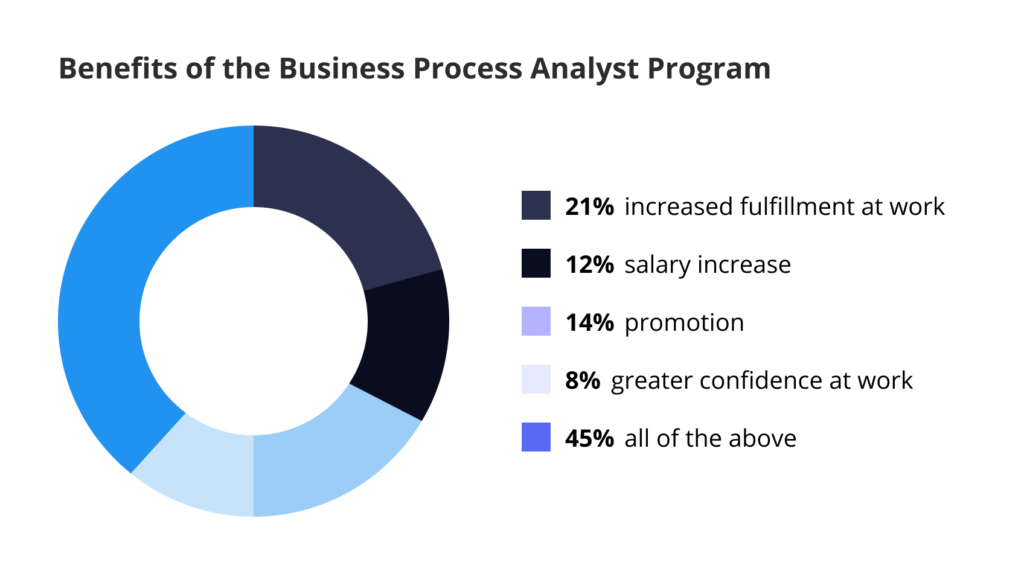
Upon program completion, you’ll be fully equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to improve team productivity and start building your career in the BA field. Here’s how individuals who enrolled in Document Workflow Automation for Business Analysts certification estimate their career benefits:
- 21% – Increased fulfillment at work
- 12% – Salary increase
- 14% – Promotion
- 8% – Greater confidence at work
- 45% – All of the above
Where does the process of business analysis meet process automation?
You may have noticed that our Document Workflow Automation for Business Analysts certification focuses on learning automation in the context of becoming a business analyst. And there’s good reason for that.
In 2023, going digital is not so much a trend but a necessity to remain competitive in the market for almost any industry. Therefore, process automation has become an integral element of maintaining workflow efficiency, which is the BA’s area of responsibility.
To show you how process automation enhances business workflows and why companies choose to hire business analysts with process automation skills, we’ve prepared several real-file examples of implementing airSlate into an organization’s daily operations.
T2 Biosystems (healthcare)
Being an emerging leader in the field of in-vitro diagnostics, T2 Biosystems faced issues connected with forms processing (e.g., inability to save partially completed forms). As a rule, medical records contain highly sensitive information. Due to the compliance process of obtaining such data, T2 Biosystems was unable to revisit a form and complete it later without restarting the entire workflow.
The airSlate workflow automation platform provided T2 with the necessary integrations for streamlining such processes. For example, the Salesforce integration enabled T2 to send out forms to their clients and automatically attach completed documents that meet compliance regulations back into Salesforce.
The automation built by airSlate allowed T2 Biosystems to remove many manual steps, save employee time, streamline its processes, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Claremont Graduate University (education)
The key issue the Claremont Graduate University was facing concerned sending paper documents back and forth, which resulted in errors, misplaced signatures, and time and money lost. On average, it would take from three to six weeks to get an employment contract completed and signed. Besides, due to the huge amount of paper documents, file management and storage were also a heavy challenge.
To start, airSlate allowed CGU to go paperless. As a result, physical document sorting and storage issues were resolved. Another benefit was that CGU could now send dozens of contracts for signing within one day and receive completed copies by the end of the week.
These are just a few examples of how process automation helps business process analysts to accomplish their main objective — improving an organization’s business processes.
The bottom line
When a business reaches a certain size, its processes inevitably need review, alignment, and streamlining. In these continuous processes of evolution, business analysts are the true engine for making change. Research, analysis, communication skills, automation knowledge, and the right education make for the perfect package for anyone planning to become a professional business analyst.
FAQ
Business analysts work closely with IT teams. Certain technical skills, as well as computer knowledge, are among the job requirements for a BA. That’s why a business analyst is often considered a technical role within an IT department. In other words — an IT process analyst.
The short answer is “no”. BA specialists collaborate with developers and other tech professionals but business analysts are not directly involved in programming or coding.
Definitely yes. It offers a variety of job opportunities and competitive salaries. Besides, business analysts generally report good work-life balance and high job satisfaction.
It depends on whether you prefer working with statistics and numbers or you’re more of a business-minded type of person. If you are more of the former, becoming a data analyst would probably be the better fit. If you are more of the latter, becoming a business analyst would certainly be more suitable. However, you can start as a BA and then move into data analysis, since many of the skills overlap.
Business analysts work on examining and analyzing an organization’s business processes, whereas business process analysts are involved in the operational aspects of these processes.
To be a business process analyst, you need strong analytical skills, understanding of business operations, and proficiency in process modeling and analysis tools. A background in business, management, or related fields, along with communication skills, is essential for this role.
A business analyst focuses on overall business needs and solutions, while a business process analyst specifically analyzes and improves business processes within an organization. The latter is a specialized role within the broader field of business analysis.
A process analyst role can be IT-related, but it is not exclusively an IT job. Process analysts work across various industries, improving and optimizing business processes, which can include IT processes but also extend to non-technical areas like finance, operations, and customer service.
- How much does a business process analyst earn?
- Which factors influence business analyst salary?
- Types of business analyst jobs
- What does a process analyst do?
- Who is a good fit for business process analyst jobs?
- What does the Document Workflow Automation for Business Analysts certification cover?
- Where does the process of business analysis meet process automation?
- The bottom line
- FAQ